A Humanoid Robot is on its Way from Mobileye Founder, and the world is watching. The founder of Mobileye, a company synonymous with autonomous driving technology, has set his sights on a new frontier: humanoid robotics. This ambitious venture promises to reshape industries and alter our interactions with technology in ways we’ve only imagined in science fiction. Imagine robots with human-like dexterity and intelligence, capable of performing complex tasks and interacting seamlessly with us.
The robot, still in its early stages of development, is already generating buzz. Its creators envision a future where these robots can assist us in a myriad of ways, from healthcare and manufacturing to customer service and education. The potential is vast, and the implications for society are far-reaching.
The Mobileye Founder and Robotics
Amnon Shashua, the visionary behind Mobileye, a leading company in autonomous driving technology, is now venturing into the world of humanoid robotics. This move signifies a significant shift in the industry, promising to bring the benefits of advanced AI and robotics to a wider range of applications.
The History of Mobileye and its Founder
Mobileye, founded in 1999, has revolutionized the automotive industry by developing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that use computer vision and machine learning to enhance safety and improve driver experience. Shashua’s expertise in computer vision and deep learning has been instrumental in Mobileye’s success. The company’s technology is now integrated into millions of vehicles worldwide, contributing to a significant reduction in road accidents.
The Founder’s Motivations for Humanoid Robotics
Shashua’s foray into humanoid robotics stems from his belief that these robots have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics. He envisions a future where humanoid robots can seamlessly interact with humans, performing tasks that are currently dangerous, repetitive, or require specialized skills.
The Potential Impact of Humanoid Robots
The development of humanoid robots by Mobileye has the potential to significantly impact various industries:
- Automotive Industry: Humanoid robots can play a crucial role in automotive manufacturing, performing complex assembly tasks with greater precision and efficiency than humans. They can also be used in vehicle testing and maintenance, enhancing safety and reducing costs.
- Healthcare: Humanoid robots can assist healthcare professionals in tasks such as patient care, surgery, and rehabilitation. They can also provide companionship and support to elderly and disabled individuals, improving their quality of life.
- Manufacturing: Humanoid robots can be deployed in manufacturing facilities to perform tasks that are hazardous or repetitive, such as welding, painting, and assembly. This can lead to increased productivity, improved safety, and reduced costs.
- Logistics: Humanoid robots can automate tasks in logistics, such as warehousing, order fulfillment, and delivery. They can work alongside humans to improve efficiency and accuracy, reducing the need for manual labor.
The Humanoid Robot’s Capabilities: A Humanoid Robot Is On Its Way From Mobileye Founder
This cutting-edge humanoid robot, a product of Mobileye’s founder’s vision, is designed to be a versatile and adaptable companion, capable of interacting with humans in a natural and intuitive way. Its capabilities encompass a wide range of physical, sensory, and cognitive functions, making it a remarkable achievement in the field of robotics.
Physical Design
The robot’s physical design is meticulously engineered to facilitate its interaction with the human world. It is designed to be approximately the size of an average human adult, standing at about 5’10” (1.78 meters) tall and weighing around 150 pounds (68 kilograms). This size and weight allow for a natural interaction with human environments and objects, enabling the robot to navigate comfortably in homes, offices, and public spaces.
The robot’s mobility is achieved through a sophisticated system of actuators and sensors. Its limbs are equipped with multiple degrees of freedom, allowing for a wide range of motion and flexibility. The robot can walk, run, jump, and even perform complex tasks that require fine motor skills, such as opening doors, picking up objects, and using tools.
Sensory Capabilities
The robot is equipped with a comprehensive suite of sensors that allow it to perceive its surroundings and interact with the world in a human-like manner.
Vision
The robot’s vision system is based on advanced computer vision technology, incorporating multiple high-resolution cameras and depth sensors. This allows the robot to see in 3D, recognize objects and faces, and understand the layout of its environment. It can even interpret body language and facial expressions, providing a more nuanced understanding of human behavior.
Hearing
The robot’s hearing system is equipped with multiple microphones, allowing it to accurately detect and process sound from different directions. It can recognize speech, filter out background noise, and even distinguish between different voices. This enables the robot to engage in conversations, understand instructions, and respond appropriately to various auditory cues.
Touch
The robot’s touch sensors are strategically placed throughout its body, allowing it to detect physical contact and understand the texture, shape, and temperature of objects. This enables the robot to handle delicate objects with care, perform tasks that require precise manipulation, and even feel emotions through physical contact.
Cognitive Abilities
The robot’s cognitive abilities are powered by advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, allowing it to learn, adapt, and interact with humans in a meaningful way.
Learning and Adaptation
The robot’s AI system is capable of continuous learning, constantly updating its knowledge base and refining its decision-making processes. This is achieved through a combination of machine learning algorithms and deep neural networks, enabling the robot to adapt to new situations, learn from its experiences, and improve its performance over time.
Human Interaction
The robot is designed to interact with humans in a natural and intuitive way, using its sensory and cognitive abilities to understand human behavior and respond accordingly. It can engage in conversations, follow instructions, and even provide emotional support. The robot’s ability to understand and respond to human emotions makes it a potentially valuable companion for individuals who may need assistance or companionship.
Potential Applications of the Humanoid Robot
The humanoid robot, with its advanced capabilities, holds immense potential to revolutionize various industries and aspects of our lives. Its human-like form and sophisticated AI allow it to interact with the world in ways previously unimaginable, opening up a vast array of applications.
Healthcare
Humanoid robots can play a crucial role in enhancing healthcare delivery.
- Patient Care: They can provide companionship and assistance to patients, reducing loneliness and improving their well-being. For example, robots can assist with daily tasks such as feeding, bathing, and medication reminders, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex care needs.
- Surgical Assistance: Robots can assist surgeons during complex procedures, offering enhanced precision and minimizing human error. For example, robotic arms can perform delicate tasks with greater accuracy than human hands, leading to faster recovery times and improved outcomes.
- Telemedicine: Humanoid robots can serve as telepresence platforms, allowing doctors to remotely examine and treat patients in remote areas or those with limited mobility. This can expand access to healthcare and reduce the need for travel.
The benefits of using humanoid robots in healthcare include improved patient care, increased efficiency, and reduced costs. However, challenges include ethical considerations, ensuring patient privacy, and the need for robust safety protocols.
Manufacturing
Humanoid robots can automate various tasks in manufacturing, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Assembly Line Work: Robots can perform repetitive and physically demanding tasks on assembly lines, reducing human fatigue and errors. They can also work in hazardous environments, protecting human workers from potential risks.
- Quality Control: Robots equipped with advanced sensors can inspect products for defects, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste. This can improve efficiency and reduce the need for manual inspection.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Robots can be used for tasks such as picking and packing, transporting goods, and managing inventory. This can optimize warehouse operations and reduce labor costs.
The benefits of using humanoid robots in manufacturing include increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved product quality. However, challenges include the need for significant investment in robotics technology, retraining workers, and ensuring safety in human-robot collaboration.
Customer Service
Humanoid robots can enhance customer service by providing personalized and efficient interactions.
- Retail and Hospitality: Robots can greet customers, answer questions, and provide product recommendations, enhancing the customer experience. They can also assist with tasks such as check-in, check-out, and ordering.
- Call Centers: Robots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. They can also provide 24/7 customer support, ensuring prompt and efficient responses.
- Information Desk: Robots can provide information and guidance to visitors in public spaces, such as museums, airports, and hospitals. This can improve the visitor experience and reduce wait times.
The benefits of using humanoid robots in customer service include improved customer satisfaction, reduced wait times, and increased efficiency. However, challenges include ensuring that robots can understand and respond to complex customer inquiries, and maintaining a human touch in interactions.
Education, A humanoid robot is on its way from mobileye founder
Humanoid robots can revolutionize education by providing personalized and engaging learning experiences.
- Interactive Learning: Robots can serve as interactive tutors, providing personalized instruction and adapting to the individual needs of students. They can also create immersive and engaging learning environments.
- Special Needs Education: Robots can provide support and assistance to students with disabilities, promoting their inclusion and fostering their learning. They can also assist with communication and mobility challenges.
- Language Learning: Robots can be used as language learning companions, providing interactive and engaging lessons. They can also help students practice their language skills in a safe and supportive environment.
The benefits of using humanoid robots in education include personalized learning, improved engagement, and enhanced accessibility. However, challenges include ensuring that robots can provide high-quality education, promoting ethical use, and ensuring equitable access for all students.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
The development and deployment of humanoid robots raise significant ethical concerns and have the potential to profoundly impact society. These robots, with their human-like appearance and capabilities, blur the lines between humans and machines, prompting questions about their role in our lives, the implications for human employment, and the potential for unintended consequences.
Ethical Concerns
The ethical considerations surrounding humanoid robots are complex and multifaceted. These robots, with their ability to mimic human behavior and interact with the world in a way that is increasingly indistinguishable from humans, present a range of ethical challenges that require careful consideration.
- Autonomy and Decision-Making: As humanoid robots become more sophisticated, they will inevitably be equipped with advanced decision-making capabilities. This raises concerns about the ethical implications of delegating critical decisions to machines, particularly in situations where human judgment and empathy are essential.
- Privacy and Surveillance: Humanoid robots, equipped with sensors and cameras, could potentially gather vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and surveillance. The ethical use and protection of this data are crucial considerations.
- Bias and Discrimination: The algorithms and data used to train humanoid robots could inadvertently perpetuate existing societal biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes. It is essential to ensure that these robots are developed and deployed in a way that promotes fairness and equity.
- Human-Robot Relationships: The increasing interaction between humans and humanoid robots could have significant implications for human relationships. The potential for emotional attachments to robots and the blurring of boundaries between human and machine relationships raise ethical questions about the nature of human connection.
- Responsibility and Liability: In the event of accidents or harm caused by humanoid robots, questions arise about who is responsible – the manufacturer, the operator, or the robot itself? Establishing clear legal frameworks for liability is essential.
Impact on Employment
The rise of humanoid robots could have a significant impact on employment, potentially displacing human workers in certain sectors. While these robots could also create new job opportunities in areas like robotics engineering and maintenance, the overall impact on the workforce remains uncertain.
- Job Displacement: Humanoid robots, with their ability to perform tasks efficiently and reliably, could potentially automate jobs currently performed by humans. This could lead to job losses in industries such as manufacturing, customer service, and healthcare.
- New Job Creation: The development and deployment of humanoid robots will also create new job opportunities in fields related to robotics engineering, software development, and maintenance. These jobs will require specialized skills and knowledge, creating a demand for a skilled workforce.
- Reskilling and Upskilling: To mitigate the potential negative impacts of job displacement, it will be crucial to invest in reskilling and upskilling programs for workers. These programs can help workers adapt to the changing job market and acquire the skills necessary to thrive in a world with humanoid robots.
Impact on Social Interactions
Humanoid robots could have a profound impact on social interactions, both positive and negative. Their ability to interact with humans in a way that mimics human behavior raises questions about the future of social connections and the potential for isolation.
- Increased Social Isolation: If humanoid robots become increasingly prevalent in our lives, there is a concern that they could lead to increased social isolation. People may spend more time interacting with robots and less time with other humans, potentially weakening social bonds.
- Enhanced Social Interactions: On the other hand, humanoid robots could also enhance social interactions. They could provide companionship for the elderly, support individuals with disabilities, and facilitate communication across language barriers.
- Redefining Social Norms: The presence of humanoid robots in society could lead to a redefinition of social norms and expectations. We may need to develop new rules and etiquette for interacting with these machines, particularly in public spaces.
Potential Applications of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, addressing societal challenges and enhancing human capabilities. Their versatility and adaptability make them well-suited for a wide range of applications.
- Healthcare: Humanoid robots could assist healthcare professionals in tasks such as patient care, surgery, and rehabilitation. They could provide companionship for elderly patients and assist with daily living activities.
- Education: Humanoid robots could serve as educational assistants, providing personalized instruction and engaging students in interactive learning experiences. They could also help to bridge the gap in access to education for students in remote areas.
- Disaster Relief: Humanoid robots could be deployed in disaster relief efforts, assisting with search and rescue operations, providing medical aid, and delivering essential supplies. Their ability to navigate difficult terrain and operate in hazardous environments makes them ideal for such tasks.
- Manufacturing: Humanoid robots could automate tasks in manufacturing, improving efficiency, productivity, and safety. They could work alongside human workers, performing tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or require precision.
- Customer Service: Humanoid robots could provide customer service in retail stores, restaurants, and other businesses. They could answer questions, provide information, and assist with transactions, offering a personalized and efficient experience.
The Future of Humanoid Robotics
The field of humanoid robotics is rapidly evolving, with advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and materials science pushing the boundaries of what these machines can achieve. As researchers and engineers continue to refine these technologies, the potential for humanoid robots to transform various aspects of our lives becomes increasingly apparent.
Current State of Humanoid Robotics Research and Development
The current state of humanoid robotics research and development is marked by significant progress in various areas, including:
- Enhanced Mobility: Humanoid robots are becoming increasingly agile and capable of navigating complex environments. Advancements in locomotion algorithms, sensor technology, and actuator design have enabled robots to walk, run, jump, and even perform acrobatic maneuvers. For example, the Atlas robot developed by Boston Dynamics can perform parkour-like movements, demonstrating its impressive agility and balance.
- Improved Dexterity: Humanoid robots are gaining greater dexterity in their hands and arms, allowing them to manipulate objects with precision and perform tasks that were previously impossible. This progress is driven by the development of advanced grippers, sensors, and control systems. For instance, the SoftHand robot developed by the University of California, Berkeley, can grasp and manipulate objects with a wide range of shapes and sizes, showcasing its adaptability and dexterity.
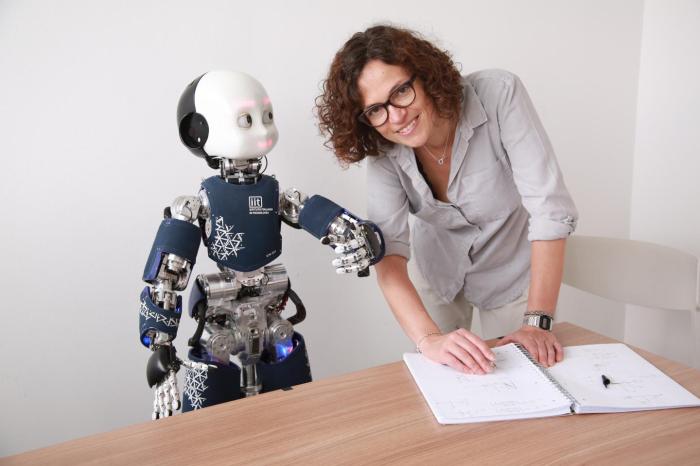
- Advanced Perception: Humanoid robots are equipped with sophisticated sensors, such as cameras, lidar, and depth sensors, enabling them to perceive their surroundings and interact with objects in a more human-like manner. These advancements in perception allow robots to navigate complex environments, recognize objects, and understand their context. For example, the iCub robot, developed by the Italian Institute of Technology, is equipped with a wide range of sensors and cameras, enabling it to perceive its environment and interact with objects in a human-like way.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms into humanoid robots is revolutionizing their capabilities. AI enables robots to learn from experience, adapt to changing environments, and make decisions based on complex information. For instance, the Sophia robot, developed by Hanson Robotics, is equipped with AI that allows it to engage in conversations, understand human emotions, and express its own emotions.
Potential Advancements and Breakthroughs in Humanoid Robotics
The coming years are expected to witness significant advancements and breakthroughs in humanoid robotics, driven by continued research and development in key areas:
- Enhanced Cognitive Abilities: AI advancements are expected to significantly enhance the cognitive abilities of humanoid robots, enabling them to perform complex tasks that require reasoning, planning, and decision-making. For example, robots could be developed to assist surgeons in complex surgeries, analyze data to make financial decisions, or even provide companionship and care to elderly individuals.
- Increased Autonomy: Future humanoid robots are likely to be more autonomous, capable of operating independently for extended periods without human intervention. This will require significant progress in areas such as navigation, object recognition, and decision-making. For example, robots could be deployed to perform tasks in hazardous environments, such as disaster zones, or explore distant planets.
- Improved Human-Robot Interaction: Humanoid robots are expected to become more intuitive and natural to interact with, enhancing communication and collaboration between humans and machines. Advancements in natural language processing, gesture recognition, and facial expression analysis will play a crucial role in this development. For example, robots could be used as personal assistants, providing information, scheduling appointments, and even engaging in meaningful conversations.
- Biologically Inspired Robotics: Researchers are exploring the use of biological materials and principles to create more advanced humanoid robots. This could lead to robots with more human-like capabilities, such as the ability to heal themselves or adapt to changing environments. For example, robots could be developed with soft, flexible materials that allow them to move and interact with their surroundings in a more natural way.
Long-Term Implications of Humanoid Robots for Humanity and Society
The widespread adoption of humanoid robots has the potential to profoundly impact humanity and society in various ways:
- Transforming Industries: Humanoid robots could revolutionize various industries, automating tasks that are currently performed by humans. This could lead to increased productivity, efficiency, and cost savings, but also raise concerns about job displacement and the need for retraining and upskilling.
- Improving Quality of Life: Humanoid robots could be used to improve the quality of life for individuals and communities. For example, robots could provide assistance to people with disabilities, care for the elderly, or even serve as companions for those who are lonely or isolated.
- Addressing Societal Challenges: Humanoid robots could be deployed to address various societal challenges, such as climate change, environmental pollution, and natural disasters. For example, robots could be used to monitor and clean up polluted areas, or even assist in rescue operations during natural disasters.
- Ethical Considerations: The development and deployment of humanoid robots raise a number of ethical considerations, such as the potential for misuse, the impact on human autonomy, and the need for responsible AI development. It is crucial to establish ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that humanoid robots are used for good and do not pose a threat to humanity.
As we stand on the cusp of this technological revolution, it’s important to consider the ethical implications and societal impact of humanoid robots. While the possibilities are exciting, we must proceed with caution, ensuring that these robots are developed and deployed responsibly. The future of humanoid robotics is brimming with potential, but it’s a future we must shape with careful consideration and foresight.
While the world waits for the arrival of a humanoid robot from Mobileye’s founder, a different kind of revolution is happening in the digital world. Apple has loosened its grip on the App Store, finally allowing retro game emulators globally, a move that could potentially open the door for more creative and innovative apps. This shift could be a sign of things to come, paving the way for a more open and diverse app ecosystem, much like the exciting possibilities of a humanoid robot.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News