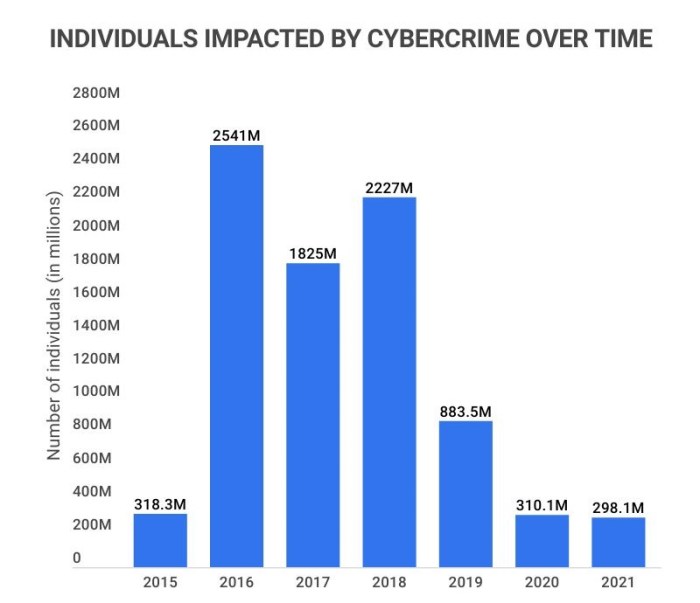
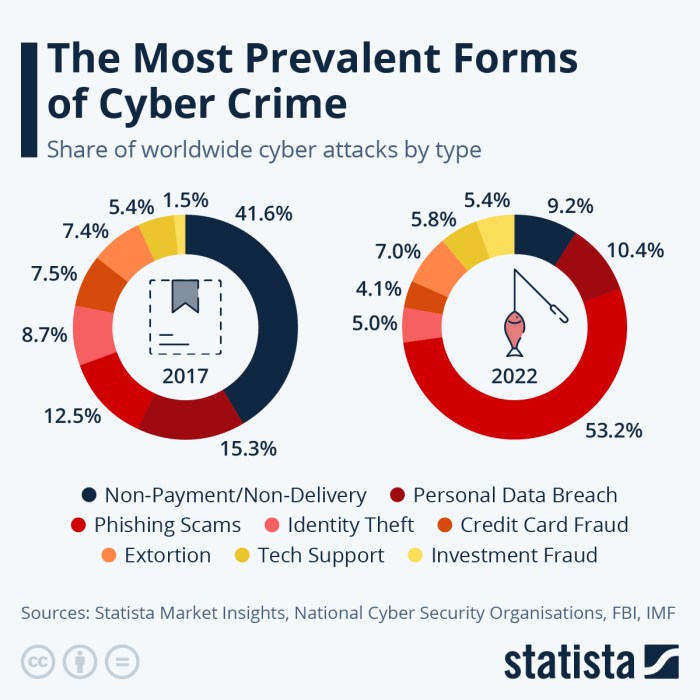
Cyber criminals 2023: they’re not just lurking in the shadows anymore. They’re evolving, adapting, and getting bolder. From sophisticated phishing schemes to ransomware attacks that cripple entire businesses, the digital landscape is becoming increasingly perilous. It’s a constant game of cat and mouse, with cybercriminals constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and steal valuable data.
The motivations behind these attacks are diverse, ranging from financial gain to political activism. But one thing’s for sure: the impact on individuals, businesses, and even governments is real and growing. As technology advances, so do the tools and techniques at the disposal of cybercriminals. It’s a battle that’s being fought on a global scale, and understanding the evolving nature of cybercrime is essential for staying ahead of the curve.
The Evolving Landscape of Cybercrime in 2023: Cyber Criminals 2023
The year 2023 witnessed a significant shift in the cybercrime landscape, with attackers becoming more sophisticated, organized, and relentless in their pursuit of sensitive data and financial gain. This evolution has been driven by factors such as the increasing reliance on technology, the emergence of new attack vectors, and the growing availability of cybercrime tools and services.
Emerging Cybercrime Trends
The evolving landscape of cybercrime in 2023 has seen a rise in new and sophisticated threats. Here are some of the major trends observed:
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks continued to be a major threat in 2023, with attackers targeting critical infrastructure, healthcare organizations, and businesses of all sizes. The attacks often involve data encryption and extortion, demanding payment in cryptocurrency to unlock the data.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers have increasingly targeted supply chains, exploiting vulnerabilities in software or hardware to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt operations. This approach allows attackers to reach a wider range of victims through a single compromised point.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Powered Attacks: The use of AI in cybercrime is becoming increasingly prevalent. Attackers are using AI to automate tasks, improve the effectiveness of phishing attacks, and even create new malware.
- Cryptojacking: This type of attack involves hijacking computer resources to mine cryptocurrency without the owner’s knowledge or consent. Cryptojacking attacks are often carried out through malicious websites or software.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering attacks are becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect. Attackers use various techniques, such as impersonation, phishing, and baiting, to trick victims into revealing sensitive information or granting access to their systems.
Adapting Tactics and Strategies
Cybercriminals are constantly adapting their tactics and strategies to stay ahead of security measures. Here are some examples of how they are evolving:
- Use of Dark Web Marketplaces: Cybercriminals are increasingly using dark web marketplaces to buy and sell stolen data, malware, and other tools. These marketplaces provide a safe and anonymous environment for criminal activity.
- Exploiting Remote Work Environments: The shift to remote work has created new opportunities for cybercriminals. Attackers are targeting home networks and devices, exploiting vulnerabilities in remote access software and VPNs.
- Targeting Mobile Devices: Mobile devices are becoming increasingly valuable targets for cybercriminals. Attackers are developing malware that can steal data, track location, and even control devices remotely.
- Using Social Media for Reconnaissance: Cybercriminals are using social media platforms to gather information about potential targets, identify their interests, and develop targeted attacks.
Examples of New and Emerging Threats
The cybercrime landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging all the time. Here are some examples of new and emerging threats observed in 2023:
- Living-off-the-Land (LOL) Attacks: These attacks leverage legitimate tools and utilities already present on a victim’s system to bypass security controls and execute malicious code.
- Zero-Day Exploits: These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor, making it difficult to patch and protect against.
- Cloud-Based Attacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting cloud environments, exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud services and applications to gain access to sensitive data.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Attacks: The growing number of connected devices has created new opportunities for cybercriminals. Attackers are targeting IoT devices, such as smart home appliances and medical devices, to gain access to networks and steal data.
The Role of Technology in Cybercrime
The rapid evolution of technology has undeniably created a fertile ground for cybercriminals. Advancements in computing power, network connectivity, and software development have not only empowered legitimate businesses but also provided sophisticated tools for malicious actors. This section will delve into how technology has become both an enabler and a weapon in the hands of cybercriminals.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies
The landscape of cybercrime is constantly shifting as cybercriminals adapt and exploit emerging technologies. Two key technologies that have significantly impacted the cybercrime landscape are artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data and automate tasks has become a double-edged sword. Cybercriminals leverage AI for various malicious purposes, including:
- Phishing: AI-powered tools can generate highly convincing phishing emails, making it harder for users to identify and avoid scams.
- Malware Development: AI can be used to create more sophisticated and evasive malware, making detection and removal more challenging.
- Social Engineering: AI-powered chatbots can mimic human conversations, enabling cybercriminals to gain trust and extract sensitive information.
- Blockchain: While blockchain technology is often associated with security and transparency, it has also attracted the attention of cybercriminals. They exploit blockchain’s decentralized nature for:
- Cryptocurrency Theft: Blockchain-based cryptocurrencies are a prime target for hackers, who use sophisticated techniques to steal digital assets.
- Dark Web Marketplaces: Blockchain provides a secure and anonymous platform for illicit activities, facilitating the sale of stolen data, malware, and other illegal goods.
- Ransomware Attacks: Blockchain can be used to create ransomware payment systems that are difficult to trace and disrupt.
Technology and Cybercrime: A Complex Relationship, Cyber criminals 2023
The relationship between technology and cybercrime is intricate and multifaceted. The following table provides a concise overview of how specific technologies contribute to the evolving landscape of cybercrime:
| Technology | Potential for Cybercrime | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Vulnerable devices can be exploited for botnets, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. | Mirai botnet, which compromised IoT devices to launch DDoS attacks. |
| Cloud Computing | Data stored in the cloud can be targeted by hackers, and misconfigurations can lead to security breaches. | Equifax data breach, which exposed sensitive information stored in the cloud. |
| Mobile Devices | Mobile apps and operating systems are susceptible to malware, phishing attacks, and data theft. | Android malware that steals banking credentials and personal information. |
| Social Media | Social media platforms are used for phishing, spreading misinformation, and manipulating public opinion. | Cambridge Analytica scandal, where user data was harvested for political manipulation. |
The Impact of Cybercrime on Society
Cybercrime has evolved into a pervasive threat, casting a long shadow over individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Its impact transcends the digital realm, rippling through the fabric of society, disrupting economies, undermining trust, and eroding fundamental rights.
The Impact on Individuals
The impact of cybercrime on individuals is multifaceted and often deeply personal. From financial losses to identity theft, the consequences can be devastating.
- Financial Losses: Phishing scams, ransomware attacks, and online fraud can lead to significant financial losses, leaving individuals struggling to recover.
- Identity Theft: Cybercriminals often target personal information, such as Social Security numbers, credit card details, and bank account information, to steal identities and commit financial fraud.
- Emotional Distress: Cyberbullying, online harassment, and the spread of misinformation can cause significant emotional distress, leading to anxiety, depression, and even suicidal thoughts.
- Loss of Privacy: Data breaches and surveillance can compromise individuals’ privacy, leading to a sense of vulnerability and a loss of control over personal information.
The Impact on Businesses
Businesses are increasingly vulnerable to cybercrime, which can disrupt operations, damage reputations, and inflict significant financial losses.
- Disruption of Operations: Ransomware attacks can cripple businesses, forcing them to shut down operations and lose revenue.
- Financial Losses: Cyberattacks can result in financial losses through stolen funds, data breaches, and reputational damage.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches and other cyberattacks can damage a company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and market share.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance Issues: Businesses face increasing legal and regulatory requirements for data security, which can be challenging and costly to comply with.
The Impact on Governments
Cybercrime poses significant challenges for governments, impacting national security, critical infrastructure, and public trust.
- National Security Threats: Cyberattacks can target critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and financial institutions, posing a threat to national security.
- Disruption of Public Services: Cyberattacks can disrupt government services, such as healthcare, education, and law enforcement, impacting citizens’ well-being.
- Erosion of Public Trust: Government data breaches and cyberattacks can erode public trust in government institutions, leading to cynicism and a sense of vulnerability.
- International Relations: Cybercrime can escalate tensions between nations, leading to diplomatic disputes and even cyberwarfare.
Potential Solutions and Preventive Measures
Addressing cybercrime requires a multifaceted approach involving collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures: Governments and businesses need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates.
- Public Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about cyber threats and best practices for online safety is crucial in empowering individuals to protect themselves.
- International Cooperation: International collaboration is essential for tackling cybercrime, including sharing information, coordinating law enforcement efforts, and developing common standards.
- Cybersecurity Legislation: Governments need to enact strong cybersecurity legislation to deter cybercrime, punish offenders, and protect victims.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, can be leveraged to detect and prevent cyberattacks.
The Future of Cybercrime
The world of cybercrime is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing reliance on digital systems. As we move forward, cybercriminals will continue to refine their tactics, exploiting vulnerabilities and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Understanding the future trends and challenges in the fight against cybercrime is crucial for individuals, organizations, and governments to stay ahead of the curve and mitigate risks.
The Rise of AI-Powered Cybercrime
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and cybercrime is no exception. AI-powered tools can be used by cybercriminals to automate attacks, improve targeting, and even create new forms of malware.
- AI-driven phishing attacks can be highly personalized and persuasive, making it harder for users to detect them.
- AI-powered malware can evade detection by traditional security software and adapt to new defenses.
- AI can be used to analyze large datasets of personal information, making it easier for cybercriminals to target individuals with tailored attacks.
This trend poses a significant challenge for cybersecurity professionals, requiring them to develop new strategies and tools to counter AI-powered threats.
The fight against cybercrime is a never-ending battle, but one that we must win. It’s not just about protecting our personal data; it’s about safeguarding the integrity of our digital world. By staying informed, adopting best practices, and embracing innovation, we can build a more secure future. The future of cybercrime is uncertain, but one thing’s for sure: we need to be prepared.
Cybercriminals in 2023 are constantly evolving their tactics, and it seems they’re finding new ways to exploit platforms like Discord. A recent incident saw a server on Discord, which coordinated costly Mastodon spam attacks , go unpunished by Discord. This raises serious questions about the platform’s ability to effectively combat malicious activity and protect its users. It’s a stark reminder that cybercriminals are always looking for new ways to wreak havoc, and we need to be vigilant in protecting ourselves from their attacks.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News