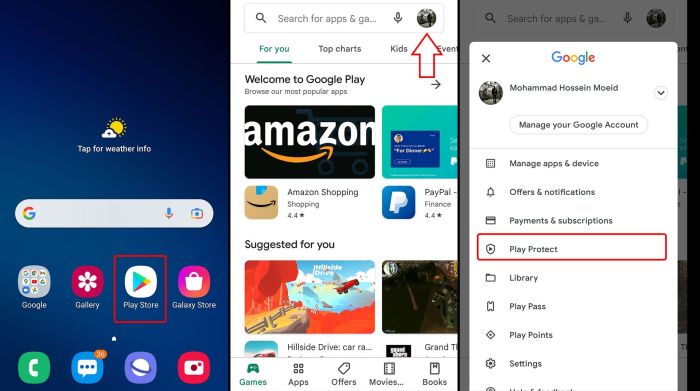
Google’s Accessibility Services
Google’s Accessibility Services are a suite of features designed to make its products and services more accessible to users with disabilities. These services aim to provide a more inclusive and equitable digital experience for everyone, regardless of their abilities.
Benefits of Google’s Accessibility Services, Google remove apps accessibility services
Google’s Accessibility Services offer numerous benefits for users with disabilities, making technology more accessible and user-friendly. These services help individuals with various disabilities, including visual impairments, hearing impairments, mobility limitations, and cognitive differences, engage with technology more effectively.
- Enhanced User Experience: Accessibility Services improve the overall user experience by providing alternative ways to interact with devices and software, making them more intuitive and usable for individuals with disabilities.
- Increased Independence: These services empower users with disabilities to perform tasks independently, reducing their reliance on others for assistance.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Accessibility Services facilitate communication and collaboration by providing tools for individuals with disabilities to express themselves and engage with others effectively.
- Greater Inclusion and Participation: By removing barriers to access, these services promote greater inclusion and participation in the digital world for individuals with disabilities.
Examples of Google’s Accessibility Services
Google offers a wide range of Accessibility Services across its platforms, including Android, Chrome, and Google Workspace. These services cater to diverse needs and disabilities, providing users with customized solutions to enhance their digital experience.
- TalkBack: This screen reader for Android devices provides spoken feedback on the user interface, allowing visually impaired individuals to navigate and interact with their devices.
- Live Caption: This feature automatically transcribes audio playing on Android devices, including videos, podcasts, and even phone calls, making content accessible for individuals with hearing impairments.
- Switch Access: This feature allows users with limited mobility to control their Android devices using external switches or other assistive technologies.
- Magnification: This feature allows users with visual impairments to enlarge the display on their Android devices, making text and images easier to see.
- Color Correction: This feature allows users with color blindness to adjust the colors on their Android devices to improve readability and accessibility.
- Accessibility Features in Google Chrome: Chrome offers features like screen readers, high-contrast mode, and keyboard navigation, enhancing accessibility for users with disabilities.
- Accessibility Features in Google Workspace: Google Workspace offers features like live captions, screen readers, and alternative input methods, making its suite of productivity tools accessible for individuals with disabilities.
Reasons for Removing Apps from Accessibility Services
Accessibility Services are powerful features designed to help users with disabilities navigate their devices. However, they can also be exploited by malicious apps. Removing apps from Accessibility Services is a crucial step in protecting your privacy and security.
Security Risks Associated with Accessibility Services
Apps granted access to Accessibility Services gain extensive control over your device. They can monitor your actions, interact with other apps, and even intercept sensitive information. This poses significant security risks, as malicious apps could exploit these privileges for nefarious purposes.
- Data Theft: Malicious apps can monitor your keystrokes, capturing passwords, credit card details, and other sensitive information. They can also intercept notifications and messages, potentially stealing valuable data.
- Unauthorized Actions: Accessibility Services allow apps to perform actions on your behalf, such as clicking buttons, opening apps, and sending messages. Malicious apps could use these capabilities to make unauthorized purchases, send spam, or even access your personal accounts.
- Privacy Violations: Apps with Accessibility Services access can monitor your usage patterns, including websites you visit, apps you use, and even the content you interact with. This information can be used for targeted advertising, data profiling, and other privacy-invasive activities.
How Malicious Apps Could Exploit Accessibility Services
Malicious apps can exploit Accessibility Services in various ways. They can use them to:
- Inject Code into Other Apps: Malicious apps can inject their code into other apps, potentially hijacking their functionality or gaining access to sensitive data.
- Bypass Security Measures: Some apps might use Accessibility Services to bypass security measures, such as two-factor authentication or password managers, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to your accounts.
- Create Accessibility Exploits: Malicious apps can create accessibility exploits, allowing them to gain control over your device without your knowledge or consent.
Privacy Concerns Related to App Access to Accessibility Services
Apps accessing Accessibility Services can collect vast amounts of personal data, potentially violating your privacy. They can:
- Track Your Activity: Apps can monitor your screen activity, including the websites you visit, the apps you use, and the content you interact with.
- Collect Personal Information: Apps can access your personal information, such as your contacts, call logs, and location data.
- Share Data with Third Parties: Apps can share your data with third parties, including advertisers, data brokers, and other companies, without your explicit consent.
Impact of Removing Apps from Accessibility Services: Google Remove Apps Accessibility Services
Removing apps from Accessibility Services can have a significant impact on users with disabilities who rely on these apps for essential functions. Accessibility services are crucial for individuals with visual impairments, motor difficulties, and cognitive challenges, enabling them to use their devices and interact with the digital world.
Impact on Users with Disabilities
The removal of apps from Accessibility Services can create significant challenges for users with disabilities. For instance, individuals who rely on screen readers to access information may lose access to critical features or content within certain apps. Similarly, users with motor impairments who rely on assistive technology to control their devices may find themselves unable to use specific apps effectively. The impact of these removals can be substantial, limiting access to vital information, communication tools, and essential services.
Examples of Affected Apps
Several apps may be affected by the removal from Accessibility Services, impacting users with disabilities.
- Screen reader apps: Apps like TalkBack (Android) and VoiceOver (iOS) are crucial for individuals with visual impairments. These apps provide audio feedback, allowing users to navigate their devices and access information. Removing apps from Accessibility Services could limit the functionality of screen readers, making it difficult for users to access certain features or content within those apps.
- Assistive touch apps: Users with motor impairments often rely on assistive touch apps to control their devices. These apps allow users to simulate touch input using gestures or other methods. Removing apps from Accessibility Services could make it difficult for users to access these assistive touch features, impacting their ability to interact with their devices.
- Text-to-speech apps: These apps are essential for users with reading difficulties or visual impairments. They convert written text into spoken words, enabling users to access information and content. Removing apps from Accessibility Services could limit the functionality of text-to-speech apps, making it challenging for users to access content within specific apps.
Challenges Faced by Users
Users with disabilities who rely on specific accessibility features face numerous challenges when apps are removed from Accessibility Services.
- Limited access to information and services: Users may lose access to essential information, communication tools, and services within specific apps. This can have a significant impact on their daily lives, limiting their ability to work, study, communicate, and access essential services.
- Difficulty using alternative solutions: Finding alternative solutions can be challenging, especially for users with specific needs. Not all apps offer alternative accessibility features, and finding suitable replacements can be time-consuming and frustrating.
- Increased dependence on assistive technology: Users may need to rely on additional assistive technology to compensate for the lack of accessibility features in certain apps. This can increase the complexity of their device setup and make it more challenging to use their devices effectively.
Google’s Approach to App Removal from Accessibility Services
Google takes a measured approach to removing apps from Accessibility Services, aiming to strike a balance between user privacy and app functionality. They employ a comprehensive process that involves rigorous criteria, transparent communication, and avenues for developers to appeal decisions.
Criteria for App Removal
Google establishes clear guidelines to determine which apps should be removed from Accessibility Services. This ensures that apps with potentially harmful or privacy-invasive behaviors are identified and addressed. Here are the key criteria:
- Unauthorized Data Collection: Apps that collect user data without explicit consent or beyond what is necessary for their intended functionality are flagged for removal. This includes collecting sensitive information like passwords, financial details, or personal messages.
- Misuse of Accessibility Features: Apps that exploit Accessibility Services for purposes other than assisting users with disabilities are targeted. Examples include apps that use accessibility features to gain unauthorized access to user devices or to perform actions without their knowledge.
- Unnecessary Accessibility Permissions: Apps that request unnecessary or overly broad accessibility permissions are also subject to removal. This ensures that apps only access the features they need to function as intended, minimizing potential privacy risks.
- User Complaints and Feedback: Google actively monitors user feedback and complaints regarding apps using Accessibility Services. Apps that receive numerous complaints about privacy violations or misuse of accessibility features are investigated and may be removed.
App Developer Appeal Process
Google provides a transparent and accessible process for app developers to appeal the removal of their apps from Accessibility Services. This process ensures that developers have an opportunity to address concerns and potentially reinstate their apps:
- Appeal Form Submission: Developers can submit an appeal form detailing the reasons why their app should be reinstated. This form requires them to explain how their app complies with Google’s Accessibility Services guidelines and address any concerns raised by Google.
- Review by Google: Google’s team reviews the appeal and investigates the app in question. They assess the developer’s arguments, analyze the app’s code and functionality, and consider any relevant evidence provided.
- Decision and Feedback: Google communicates its decision to the developer, providing clear and concise feedback on the outcome of the appeal. If the appeal is successful, the app is reinstated. If it is unsuccessful, Google provides guidance on how to modify the app to comply with the guidelines.
Communication and Support for Affected Users
Google prioritizes clear communication with users affected by app removals from Accessibility Services. They aim to ensure users understand the reasons for the removal and provide alternative solutions or guidance:
- Notification of Removal: Users are notified when an app they have installed is removed from Accessibility Services. This notification includes information about the reason for the removal and potential alternatives.
- Support Resources: Google provides users with access to support resources, such as FAQs, help articles, and contact information for further assistance. These resources aim to address user concerns and provide guidance on using alternative apps or features.
- Transparency and Accountability: Google strives to be transparent about its decision-making process and the reasons for removing apps from Accessibility Services. They aim to build trust with users by providing clear explanations and addressing concerns openly.
Alternatives to Accessibility Services
While removing apps from Accessibility Services might seem like a drastic measure, it’s essential to understand that there are alternative ways for users to access specific features and functionalities. Android offers a variety of built-in and third-party solutions that can provide similar or even enhanced accessibility experiences.
Accessibility Features Built into Android
Android has a wide range of built-in accessibility features that cater to various needs. These features are designed to be user-friendly and readily available, providing an alternative to third-party apps that might have been removed from Accessibility Services.
- Magnification: This feature allows users to enlarge portions of the screen for easier viewing. Users can adjust the magnification level, zoom in on specific areas, and even use a magnifying glass to explore the screen.
- Color Inversion: This feature inverts the colors on the screen, making it easier for users with visual impairments to distinguish text and images. It can also be helpful for users who are sensitive to certain colors.
- Live Caption: This feature automatically generates captions for audio content playing on the device, including videos, podcasts, and even phone calls. It’s a valuable tool for users who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- TalkBack: This screen reader provides spoken feedback on what’s happening on the screen, allowing users who are blind or have low vision to interact with their devices. It can read aloud text, describe images, and announce notifications.
- Switch Access: This feature allows users with limited mobility to control their devices using external switches, such as a head switch or a button. Users can navigate menus, select items, and perform actions using these switches.
Third-Party Accessibility Apps
While Android’s built-in accessibility features offer a comprehensive suite of tools, some users may prefer third-party apps for specific needs or to customize their accessibility experience.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) Apps: These apps can read aloud text from websites, documents, and other sources, providing an alternative to the default TTS engine. Some popular TTS apps include Google Text-to-Speech, IVONA, and Acapela.
- Screen Magnification Apps: These apps offer advanced magnification features, such as the ability to adjust zoom levels, customize color filters, and even use a magnifying glass to explore specific areas of the screen. Examples include Magnifier, Zoom, and Big Launcher.
- Assistive Touch Apps: These apps provide a virtual “floating button” on the screen that users can tap to access various accessibility features, such as screen magnification, color inversion, and even shortcuts to specific apps. Popular apps in this category include Assistive Touch, Floating Button, and Easy Touch.
Recommendations for Users
For users who are impacted by the removal of apps from Accessibility Services, here are some recommendations:
- Explore Android’s built-in accessibility features: Many of the features offered by third-party apps are already available within Android. Take some time to explore these options and see if they meet your needs.
- Consider using third-party apps that don’t require Accessibility Services: There are many accessibility apps available that don’t need to be granted access to Accessibility Services. These apps can provide similar functionality without raising security concerns.
- Contact the app developer: If you rely on a specific app that has been removed from Accessibility Services, reach out to the developer and inquire about alternative solutions or updates that might address the issue.
Google remove apps accessibility services – Google’s removal of apps from Accessibility Services is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While the move aims to enhance security and privacy, it also raises concerns about accessibility for users with disabilities. As we navigate this evolving landscape, it’s crucial to find solutions that balance user safety with the need for accessible technology. Open communication, transparency, and collaboration between Google, app developers, and users are key to ensuring a future where accessibility remains a top priority.
Google’s decision to remove apps’ accessibility services raises some serious questions about user privacy. While we all want technology to be more accessible, it’s crucial to ensure that these services aren’t being used to collect sensitive personal data. This brings to mind the recent advancements in AI detecting suicidal thoughts through brain scans , which raises even more ethical concerns about data privacy and the potential for misuse.
Ultimately, the focus should be on creating accessible technology that respects user privacy and doesn’t invade their personal space.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News