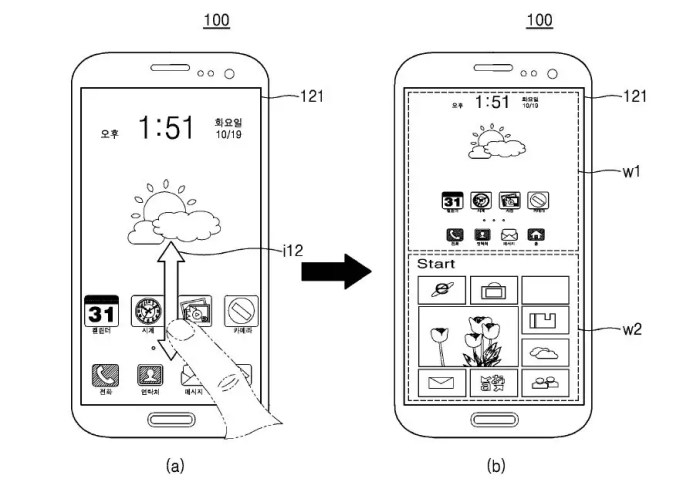
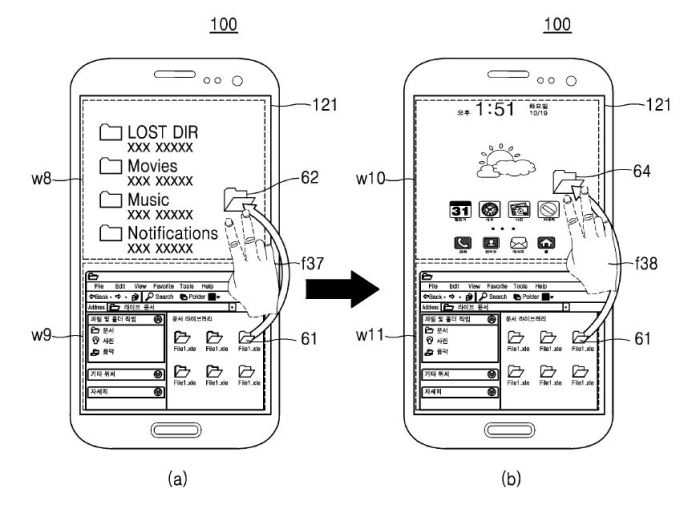
Samsung’s Dual Operating System Handset: Samsung Patents Handset That Can Run Both Android And Windows
Imagine a smartphone that seamlessly switches between the productivity power of Windows and the versatility of Android. This isn’t a futuristic dream; it’s a reality that Samsung is actively exploring with its dual operating system handset patent. This revolutionary concept promises to reshape the mobile landscape, offering users a unique blend of power and flexibility.
Benefits of a Dual Operating System Handset
A Samsung handset running both Android and Windows would offer users a plethora of advantages. The most obvious benefit is the ability to access the full range of applications available on both platforms. This means users could enjoy the extensive app libraries of both Android and Windows, maximizing their productivity and entertainment options. For instance, a user could switch to Android to play a mobile game and then seamlessly transition to Windows to work on a document. The dual operating system also allows for better multitasking capabilities. Imagine running a Windows-based productivity app alongside an Android gaming app, maximizing your time and efficiency.
Target Audience for the Dual Operating System Handset
This device caters to a diverse audience. Professionals seeking a powerful and versatile device for work and personal use would find it particularly appealing. Imagine a salesperson who needs to access work files on Windows and use Android apps for communication and research. This device would be their perfect companion. Students who rely on both platforms for their studies would also benefit from the flexibility and power offered by this device. Additionally, power users who enjoy exploring both platforms and leveraging the best of both worlds would be drawn to this innovative offering.
Market Implications of the Dual Operating System Patent
Samsung’s dual operating system patent has significant market implications. If implemented, it could disrupt the current mobile landscape, offering users a compelling alternative to existing platforms. It could potentially lead to a new era of mobile devices, where users can seamlessly transition between operating systems depending on their needs. The patent could also encourage other manufacturers to explore similar dual operating system solutions, fostering innovation and competition in the mobile market. While the exact timeline for this technology remains uncertain, its potential impact on the industry is undeniable.
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Running both Android and Windows on a single device presents significant technical challenges, requiring innovative solutions to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
Resource Management
Efficiently managing system resources like memory, storage, and processing power is crucial for smooth operation. Android and Windows have distinct resource requirements, making it essential to allocate resources effectively to prevent conflicts and ensure both operating systems function optimally.
- Memory Management: A sophisticated memory management system is needed to allocate sufficient memory to both operating systems, ensuring neither experiences performance degradation due to insufficient resources.
- Storage Management: The device must provide adequate storage space for both operating systems and their respective applications, while also managing file access and data sharing between them.
- Processor Allocation: The device’s processor must be able to efficiently switch between the two operating systems, ensuring each receives sufficient processing power for smooth operation. This may involve using virtual machines or dedicated hardware partitions.
Interoperability and Compatibility
Ensuring seamless interoperability and compatibility between Android and Windows is paramount for user experience. This includes enabling communication between applications running on different operating systems and ensuring hardware components function correctly with both platforms.
- Application Compatibility: A mechanism must be in place to ensure that applications designed for one operating system can run on the other, either through emulation or through the development of cross-platform applications.
- Hardware Compatibility: All hardware components, such as the display, touch screen, and camera, must be compatible with both operating systems, requiring careful driver development and configuration.
- Data Sharing: A robust data sharing mechanism is needed to allow users to access and manage data across both operating systems seamlessly, including sharing files, contacts, and settings.
User Interface and Experience
Providing a user-friendly and intuitive experience for navigating between Android and Windows is crucial. This involves designing a seamless switching mechanism and ensuring consistent user interface elements across both platforms.
- Switching Mechanism: The device must offer a simple and intuitive method for switching between Android and Windows, allowing users to seamlessly transition between the two environments without any significant interruptions.
- User Interface Consistency: While maintaining the distinct characteristics of each operating system, the user interface elements should be consistent across both platforms to minimize confusion and enhance usability.
- Application Integration: The device should allow users to launch and interact with applications from either operating system, ensuring a cohesive and integrated experience.
User Experience and Interface
The seamless integration of Android and Windows on a single device presents a unique opportunity to create a user experience unlike any other. A well-designed interface can make switching between operating systems feel natural and intuitive, unlocking new possibilities for users.
Interface Design for Seamless Transition
A key aspect of the user experience is the ability to transition seamlessly between Android and Windows environments. This requires a carefully crafted interface that provides a consistent and intuitive navigation experience. One approach could be to utilize a single home screen that acts as a central hub, providing access to both operating systems. This home screen could feature a dynamic layout that adapts based on the currently active OS, showcasing relevant apps and features. For instance, when Android is active, the home screen could display Android widgets and shortcuts, while switching to Windows would dynamically transition to a Windows-centric layout.
Enhanced Features and Functionalities
This dual-OS device can offer a wide range of enhanced features and functionalities that enrich the user experience. For example, the device could leverage the strengths of both operating systems by allowing users to run Android apps on Windows and vice versa. This could be achieved through technologies like virtualization or emulation, enabling users to access a wider range of applications. Another potential feature is the ability to share files and data seamlessly between Android and Windows environments. This could be facilitated through a shared file system or cloud-based storage, making it effortless to transfer documents, photos, and other data between the two operating systems.
Comparison with Existing Devices
The user experience of this dual-OS device differs significantly from existing Android and Windows devices. Unlike single-OS devices, this device offers the flexibility and convenience of using two operating systems on a single device. This eliminates the need to carry multiple devices, simplifying the user’s digital life. Furthermore, the ability to switch between operating systems on demand allows users to tailor their device to their specific needs at any given moment. For example, a user could use Android for casual browsing and entertainment while switching to Windows for work-related tasks or productivity apps. The dual-OS device provides a level of customization and versatility that is not possible with existing single-OS devices.
Market Competition and Potential Impact
The dual-OS smartphone concept isn’t entirely new. Several manufacturers have attempted to create devices that run both Android and Windows, but none have achieved widespread success. The key challenge lies in balancing the user experience and resource management between two operating systems. Samsung’s patent, however, could potentially disrupt the market by offering a seamless and efficient dual-OS experience.
Competitive Landscape
The current smartphone market is dominated by Android and iOS. While Windows Phone once held a significant share, it has declined considerably. A few manufacturers, like Microsoft, have released devices that can run both Android and Windows, but these devices have been met with mixed reception. The main reasons for their limited success include:
* Poor user experience: Switching between operating systems often involves a clunky process and can lead to compatibility issues.
* Resource limitations: Running two operating systems simultaneously can strain device resources, leading to slower performance and reduced battery life.
* Limited app availability: Users are limited to the apps available on each operating system, potentially hindering functionality and productivity.
Samsung’s patent, however, aims to address these limitations by offering a more integrated and efficient dual-OS experience. If successful, it could create a new competitive landscape in the smartphone market.
Potential Impact on the Smartphone Market
Samsung’s dual-OS smartphone could potentially have a significant impact on the smartphone market. Here are some potential scenarios:
* Increased consumer choice: Users would have the flexibility to choose between two operating systems, catering to different preferences and needs.
* Enhanced productivity: Users could seamlessly switch between operating systems to access specific apps or features, increasing productivity.
* New market segment: Samsung could create a new market segment for dual-OS smartphones, attracting users who seek the best of both worlds.
* Competition with existing players: Samsung’s dual-OS device could challenge existing smartphone manufacturers, forcing them to innovate and offer similar features.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dual-OS Devices, Samsung patents handset that can run both android and windows
Here’s a table outlining the potential advantages and disadvantages of Samsung’s dual-OS device compared to existing devices:
| Feature | Dual-OS Device | Single-OS Device |
|—|—|—|
| Operating Systems | Android and Windows | Android or iOS |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| App Availability | Wider range | Limited to one platform |
| Resource Management | Potential for resource conflicts | Efficient resource allocation |
| User Experience | Potential for seamless integration | Consistent experience within one platform |
| Cost | Potentially higher | Generally lower |
Future Implications and Potential Applications
The ability to seamlessly switch between Android and Windows on a single device opens up a world of possibilities beyond just smartphones. This dual-OS concept, with its flexibility and adaptability, can be leveraged to create innovative solutions across various device categories.
Potential Applications in Other Devices
This dual-OS concept can be implemented in various devices, extending its reach beyond smartphones.
- Laptops and Tablets: Imagine a laptop that seamlessly transitions between a powerful Windows productivity environment and a more user-friendly Android interface for entertainment and casual browsing. This could cater to diverse user needs and provide a more versatile computing experience.
- Smart Home Devices: Integrating both Android and Windows into smart home devices like smart speakers and smart displays could enable a more unified and interactive experience. Users could control their smart home devices through both Android and Windows interfaces, making it easier to manage and personalize their smart home ecosystem.
- Wearables: Integrating dual-OS in wearables like smartwatches could offer users the flexibility to choose between Android’s open ecosystem and Windows’ focus on productivity and integration with other Microsoft services.
Future Scenarios for Dual-OS Implementation
- Hybrid Work Environments: In a hybrid work environment, a dual-OS device could be invaluable, allowing users to seamlessly switch between their work and personal lives. They could use Windows for professional tasks and then transition to Android for personal communication and entertainment, all on the same device.
- Education and Training: Schools and training institutions could utilize dual-OS devices to provide students with access to both Android’s educational apps and Windows’ productivity tools. This would allow for a more comprehensive learning experience, combining interactive learning with traditional coursework.
- Accessibility for Diverse Users: Dual-OS devices could cater to diverse user needs, including those with disabilities. By providing access to both Android’s accessibility features and Windows’ assistive technologies, these devices could offer a more inclusive and accessible computing experience.
Samsung patents handset that can run both android and windows – Samsung’s dual-OS handset is more than just a tech innovation; it’s a glimpse into the future of mobile computing. By merging two powerful operating systems, Samsung could unlock a world of possibilities for users, blurring the lines between work and play, productivity and entertainment. While challenges remain, the potential of this patent is undeniable, promising a future where our smartphones can truly adapt to our every need.
Samsung’s latest patent for a handset running both Android and Windows is a bold move, showing their commitment to innovation. It’s a reminder that tech is constantly evolving, and we’re seeing AI play a bigger role in our lives, like in the fascinating new study that can ai detect depression from instagram photos. So, maybe Samsung’s dual-OS phone could even be used to help people struggling with mental health, who knows! It’s all part of the exciting future of technology.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News