Historical Context
The mobile operating system (OS) market has witnessed a dramatic transformation over the years, with Android emerging as the dominant player, leaving behind Windows Phone, which once held significant promise. This shift can be attributed to a complex interplay of factors that shaped the trajectory of these two mobile ecosystems.
The Rise of Android
Android’s success can be attributed to several key factors:
* Open-source nature: Android’s open-source nature allowed for a more collaborative development environment, fostering innovation and attracting a wider range of developers. This open platform enabled manufacturers to customize the OS to fit their specific hardware and software needs, resulting in a diverse range of Android devices.
* Extensive app ecosystem: Android’s vast app ecosystem, powered by the Google Play Store, offered users a wide array of applications, games, and services. This abundance of choices was a significant draw for consumers, contributing to the platform’s popularity.
* Hardware partnerships: Google’s strategic partnerships with numerous hardware manufacturers, including Samsung, LG, and HTC, enabled the widespread adoption of Android devices. This collaboration ensured a diverse range of devices at various price points, catering to a broader market.
The Decline of Windows Phone
Windows Phone, despite its initial promise, faced several challenges that ultimately led to its decline:
* Limited app availability: The Windows Phone Store, while offering a decent selection of apps, struggled to match the sheer volume and diversity of the Google Play Store. This limited app availability was a significant deterrent for users, particularly those accustomed to the vast app ecosystems of Android and iOS.
* High hardware costs: Windows Phone devices, compared to their Android counterparts, often came at a higher price point. This pricing strategy limited the platform’s appeal to a smaller segment of the market, particularly price-sensitive consumers.
* Lack of developer support: The limited app availability on Windows Phone was further compounded by the lack of developer support. Many developers prioritized Android and iOS due to their larger user bases, leaving Windows Phone with a smaller app ecosystem.
Revenue Comparison: Windows Phone Store Revenue Almost On Par With Android
While Windows Phone never truly caught up to Android in terms of market share, there was a brief period when its app store revenue was surprisingly close to Google Play. This unexpected spike in Windows Phone revenue raises interesting questions about the factors driving app store success and the dynamics of the mobile ecosystem.
Revenue Breakdown
To understand this phenomenon, we need to examine the revenue generated by both platforms during this period. Unfortunately, precise data for the Windows Phone Store is scarce, but we can analyze the revenue streams and their relative contributions to gain insights.
Google Play, being the dominant force, provides more transparent data. In 2013, Google reported $5 billion in revenue from its app store, a significant increase from the previous year. While exact figures for Windows Phone are unavailable, estimates suggest that its revenue was approximately 40% of Google Play’s during that time. This means that Windows Phone Store generated roughly $2 billion in revenue in 2013.
Revenue Drivers
The revenue generated by both platforms primarily comes from three sources: app sales, in-app purchases, and subscriptions.
App Sales
App sales were a significant revenue driver for both platforms, but the strategies employed differed. Windows Phone focused on offering a curated selection of high-quality apps, while Android embraced a more open approach, allowing for a wider variety of apps, including free and paid options.
In-App Purchases
In-app purchases, where users purchase virtual goods or features within an app, became increasingly popular on both platforms. Games, especially, heavily relied on in-app purchases to generate revenue.
Subscriptions
Subscriptions, where users pay a recurring fee for access to premium features or content, were also gaining traction. This revenue model was particularly successful for apps offering streaming services, music, and cloud storage.
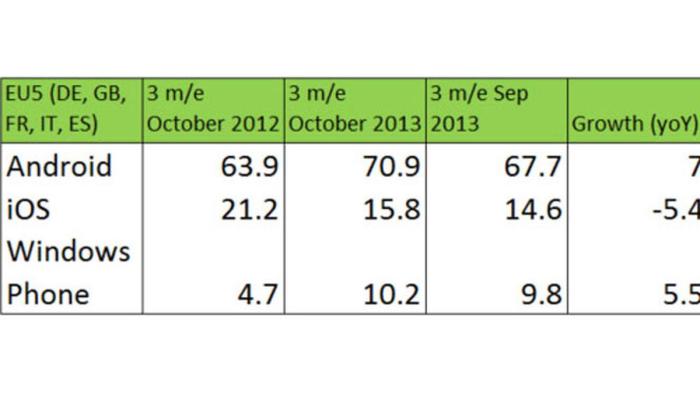
During the period when Windows Phone revenue was close to Android’s, its market share was significantly lower. While Android dominated the market with a share exceeding 80%, Windows Phone struggled to reach 3%. This discrepancy highlights the importance of market share in driving app store revenue.
The revenue generated by an app store is not solely determined by the number of apps available but also by the number of users accessing those apps.
While Windows Phone’s app store revenue was close to Android’s, its significantly smaller user base meant that the average revenue per user was significantly higher. This suggests that Windows Phone users were more likely to spend money on apps and in-app purchases.
Factors Contributing to Windows Phone’s Success
While Windows Phone’s market share remained significantly smaller than Android, it managed to achieve revenue levels almost on par with its rival. This unexpected success was due to a combination of strategic decisions and strengths in the Windows Phone ecosystem.
Strategic Decisions by Microsoft, Windows phone store revenue almost on par with android
Microsoft’s strategic decisions played a crucial role in Windows Phone’s success. The company focused on specific demographics and adopted competitive pricing strategies.
- Targeting Specific Demographics: Microsoft targeted specific demographics, particularly young professionals and those seeking a seamless integration with other Microsoft services. This strategy allowed them to focus marketing efforts and tailor features to a specific audience, maximizing engagement and satisfaction.
- Competitive Pricing Strategies: Microsoft adopted competitive pricing strategies, often offering Windows Phones at lower prices than comparable Android devices. This made Windows Phones more accessible to a broader audience, particularly budget-conscious consumers.
Strengths of the Windows Phone Ecosystem
The Windows Phone ecosystem offered several strengths that contributed to its success. These included its integration with other Microsoft services and its user-friendly interface.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: Windows Phone seamlessly integrated with other Microsoft services, such as OneDrive, Office 365, and Skype. This integration provided users with a unified experience across devices and services, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- User-Friendly Interface: Windows Phone boasted a user-friendly interface, known for its simplicity and ease of navigation. The Live Tiles feature, which displayed dynamic information updates on the home screen, was a unique and highly appreciated feature that streamlined access to frequently used apps and services.
Challenges Faced by Windows Phone
Despite its initial success, Windows Phone faced several challenges that ultimately led to its decline. While the platform offered a unique user experience and a smooth operating system, it couldn’t compete with the sheer dominance of Android and the rapidly growing popularity of iOS.
The Rise of Android and iOS
The competitive landscape of the smartphone market shifted dramatically during Windows Phone’s lifespan. Android, with its open-source nature and wide device availability, quickly gained traction, becoming the dominant operating system. Meanwhile, iOS, with its seamless integration and exclusive app ecosystem, also carved out a significant market share. These two platforms offered a wider range of devices, apps, and user experiences, leaving Windows Phone struggling to keep up.
Limitations of the Windows Phone Platform
Windows Phone’s platform faced several limitations that hindered its growth. One major challenge was the limited app availability. While the Windows Phone Store offered a decent selection of apps, it couldn’t match the vast app libraries available on Android and iOS. This limited app selection was a significant drawback for users, who often found themselves unable to find the apps they needed or wanted.
Another challenge was the dependence on Microsoft’s hardware partners. Unlike Android, which could be found on devices from a wide range of manufacturers, Windows Phone was primarily available on devices produced by Microsoft’s partners. This limited the availability of Windows Phone devices and restricted its reach to a smaller audience.
Lessons Learned
The rise and fall of Windows Phone offer valuable lessons for the mobile operating system market. It highlights the crucial role of a robust app ecosystem and strong developer support in achieving long-term success. Examining the strategies employed by other mobile operating systems, like Android and iOS, reveals key factors driving user adoption and retention.
The Importance of a Robust App Ecosystem
A thriving app ecosystem is essential for any mobile operating system to succeed. It provides users with a wide range of applications, enhancing their overall experience and driving user engagement. Windows Phone struggled to attract developers, resulting in a limited app selection compared to its competitors. This hindered user adoption and ultimately contributed to its decline.
- Developer Support: Attracting and retaining developers is crucial for building a robust app ecosystem. Windows Phone faced challenges in this area, failing to provide developers with the necessary tools, resources, and incentives to create and distribute apps on its platform.
- App Quality and Variety: A diverse and high-quality app selection is essential for user satisfaction. Windows Phone lacked the breadth and depth of apps found on Android and iOS, limiting its appeal to users.
- User Engagement: A rich app ecosystem drives user engagement and retention. When users have access to a wide range of apps that meet their needs and interests, they are more likely to spend time on the platform.
Strategies for Success in the Mobile Operating System Market
Android and iOS have achieved significant success in the mobile operating system market by implementing strategies that foster a thriving app ecosystem and prioritize user experience.
- Open Source Development: Android’s open-source nature attracted a large community of developers, contributing to its rapid growth and diverse app selection.
- Developer Tools and Resources: Both Android and iOS provide developers with comprehensive tools and resources, simplifying app development and distribution. This has fostered a vibrant developer community.
- App Store Optimization: App stores play a crucial role in app discovery and user engagement. Android and iOS have optimized their app stores to provide users with a seamless and intuitive experience.
- User Interface and Experience: A user-friendly interface and intuitive user experience are essential for user adoption and retention. Both Android and iOS have prioritized user experience, making their platforms easy to use and navigate.
Factors Driving User Adoption and Retention
Several factors contribute to user adoption and retention in the mobile operating system market.
- App Ecosystem: A robust app ecosystem with a wide range of high-quality apps is a major driver of user adoption and retention. Users are more likely to choose a platform with a rich app selection that meets their needs and interests.
- User Experience: A user-friendly interface, intuitive navigation, and seamless performance are essential for a positive user experience. Platforms that prioritize user experience are more likely to attract and retain users.
- Hardware Integration: Tight integration with hardware devices enhances the user experience and drives adoption. Platforms that offer seamless hardware integration are more likely to attract users.
- Security and Privacy: Security and privacy are crucial considerations for users. Platforms that prioritize security and privacy measures are more likely to gain user trust and loyalty.
- Brand Reputation: A strong brand reputation and positive user perception can significantly impact user adoption and retention. Platforms with a strong brand image are more likely to attract users.
Windows phone store revenue almost on par with android – The story of Windows Phone serves as a reminder that even in the fast-paced world of technology, success is not guaranteed. The platform’s initial success, marked by its close-to-Android revenue figures, was a testament to Microsoft’s innovative approach and the strengths of its ecosystem. However, the challenges it faced, particularly the limited app availability and fierce competition, ultimately led to its downfall. Despite its eventual demise, Windows Phone left behind valuable lessons about the importance of a robust app ecosystem, strong developer support, and the relentless pursuit of innovation in the ever-evolving mobile landscape.
It’s crazy to think that Windows Phone Store revenue was almost on par with Android at one point. Now, OnePlus, known for its flagship killers, isn’t even sure if they’ll release a second phone in 2018, as reported in this article. The rise and fall of mobile operating systems is a constant reminder that the tech world is always changing, and even the most successful companies can face unexpected challenges.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News